Introduction
As a business leader, you know how important it is to ensure that the technical side of your organisation is running smoothly and efficiently.
However, do you know if the right technology decisions have been made to support the future?
If you are a startup looking for seed funding or a company going through a merger or acquisition, you will be asked to answer this question at some stage. Proactively reviewing your business and systems and making any needed changes can drive value within your organisation. This will help you in future deals and keep you abreast of market and technology trends.
In this blog post, we’ll look in detail at what technical due diligence is, as well as walk through some best practices to maximise your success.
Contents
PART I
1. What is technical due diligence?
2. When is technical due diligence needed?
3. Why is technical due diligence important now?
4. Who conducts technical due diligence?
5. What is the technical due diligence process?
PART II
1. Technical due diligence key considerations
2. What are tech due diligence challenges?
3. How long does a technical due diligence review typically take?
PART III
1. Terms frequently used in this post
PART I
What is technical due diligence?
Technical due diligence is the term used to describe a thorough and independent review of people, processes, and technology within a business. This undertaking serves to both support any future investment decisions as well as improve overall business outcomes.
The due diligence process aims to give your business an extensive evaluation of its entire organisation, not just your IT systems. This enables you to effectively identify opportunities, form strategies, plan projects, forecast results, understand the risks present, and make sound investment decisions. At the heart of it lies a structured, comprehensive assessment that gives investors, principals, and shareholders more confidence in their choices.
By undertaking technical due diligence, you can maximise your efforts by obtaining significant knowledge of the IT and business operations at each level of your organisation’s activity.
When is technical due diligence needed?
Various reasons may prompt technical due diligence. This includes all types of investment (from seed fund to series C), mergers and acquisitions (M&A), or even an internal assessment for identifying digital transformation opportunities that maximise shareholder value.
Each party is looking to answer the same questions:
- How much is your business worth?
- How much can it be worth in the future?
- Is your organisation equipped to deliver on all its promises?
- Are you trying to overstate your current position?
No matter the reason, investors/stakeholders will want to thoroughly evaluate your business and technology before making any commitment. This often includes detailed evaluations to confirm they know precisely what they are getting into and ensure there is no reasons not to proceed.
Navigating the process can be complex, drawn out, and extremely taxing – given how important a deal may be. However, if you plan adequately, it can be a straightforward and insightful exercise.
Why is technical due diligence important now?
The latest Gartner research reveals that most CEOs are boosting investments in digital to counter current economic issues such as inflation, thinning talent pool and supply constraints.
To support this, conducting comprehensive tech due diligence to identify potential risks and opportunities is essential and can aid in creating business worth through technology. In times of economic hardship, enterprises should be confident that their IT investments are adequate and suitable for their organisation’s objectives.
As we will analyse further, tech due diligence picks up the topics that traditional commercial due diligence would miss, including:
- Identify areas for improvement: A quality technical foundation is essential for performance and can significantly impact your scalability potential.
- Identify architecture weaknesses: Revitalising an ageing platform/product requires significant expertise and effort to update it.
- Identify team inefficiencies and critical dependencies: Organisations that rely on specific capabilities and proprietary knowledge should take extra care in conducting a comprehensive people risk evaluation.
- Identify your strengths: Unearth the most profitable possibilities within your enterprise. Establish an organisational architecture that will accomplish your most critical corporate objectives efficiently and effectively.
Who conducts technical due diligence?
Usually, an investor/principal starts the tech due diligence process and sets the scope and timeframe of the review.
To ensure this runs smoothly and efficiently, this is generally undertaken by an external third-party expert with a strong understanding of both the market and the technology used. Such firms should have experience in assessing complex systems and services used within a company’s IT operations and will be able to provide a holistic overview of your company.
What is the Technical Due Diligence Process?
Even though the technical diligence process may vary based on specific engagements, the technical aspect of the process usually follows the same framework.
The technical due diligence process will include the following stages:
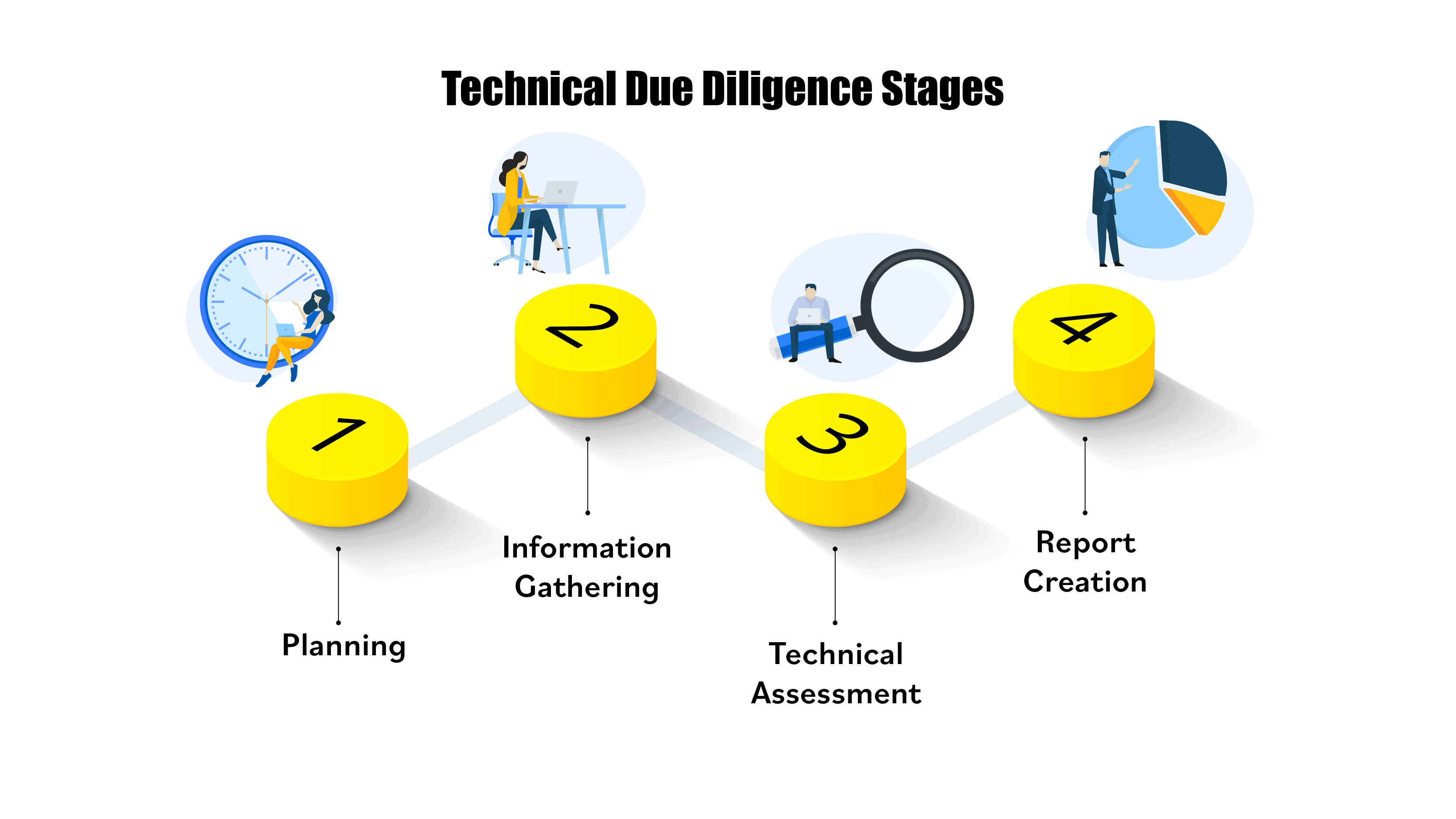
Stage 1: Planning the Assessment

The first and foremost step involves creating a checklist to determine what areas should be covered during the technical due diligence process and how much time will be devoted to each task.
Before any due diligence process can be conducted, you and your stakeholders/potential investors must come to a mutual agreement regarding all facets of the review, such as:
-
-
- The timeline for each step of the process.
- The scope of the data, assets, and software for disclosure.
- Quantifying the necessary number of key personnel to interview.
- How to access pertinent systems, product development environments, and documentation.
-
By establishing these terms, your company should compile all related documentation for detailed examination. To ensure that records are confidential, I strongly suggest you store and share files through a secure cloud platform with the assigned tech due diligence team.
This platform can also be used to manage Q&A activity in stage three.
Key elements:
In the case of an M&A or start-up investment, a Letter of Intent (LOI) is usually signed before the due diligence can begin. This LOI outlines how each company will conduct their research to move towards finalising an agreement. To protect the privacy of all involved, a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) is also signed by all parties.
Stage 2: Collection of documentation and information

This stage involves collating all the documentation and data relevant to its technical operations, such as IT architectural descriptions and diagrams, infrastructure specs, development code base, backup and recovery facilities, server documentation, and development procedures.
It will also be necessary to grant the tech due diligence team access to primary systems in readiness for investigation. Expect your team members to support a code review of any internally built software development, as ascertaining the code quality is an essential objective of any tech diligence.
To ensure a smooth and successful assessment, assign one or more individuals to manage the process and promptly provide the necessary documentation.
Key Elements:
In my experience, supporting the due diligence team is very important, as you want to make their job as easy as possible. This sets the tone for the coming stages and gives the tech due diligence analysts a good feel for your team’s culture and calibre/competency.
Stage 3: Technical Assessment
Having collected all essential documents and information, the Tech Due Diligence team can examine the company’s technological infrastructure and architecture to assess how it aligns with your overall company objectives.
After the analysts have completed studying your documents, they will often want to observe your IT systems and procedures. This includes desktop reviews assessing how well your platform functions. Moreover, during this stage, the Tech Due Diligence team will likely interview technical directors and key personnel involved with these operations.
Your staff must provide answers to any questions. You should expect several rounds of probing questions as the tech due diligence team seeks a complete understanding, so be prepared.
Key element:
Ensure you properly arm your colleagues with all relevant information so they can describe your technology and explain why certain technologies were chosen over others at a given time.
They must understand the context in which those decisions were made. It may not always be evident from solely looking at documents, and although hindsight can show us how things could have been done differently, sometimes our options are limited.
Stage 4: Report Creation

At the end of the process, an objective report detailing the findings will be produced, including recommendations and remediations to help inform decisions.
This report will cover the worth of your IT systems, the condition of your assets, discovered flaws, possible risks, and recommended actions.
Key element:
The due diligence report will contain a wealth of information and will usually conclude with a recommendation section. Your senior leaders should use this to help shape plans and future investments.
PART II
Technical due diligence key considerations
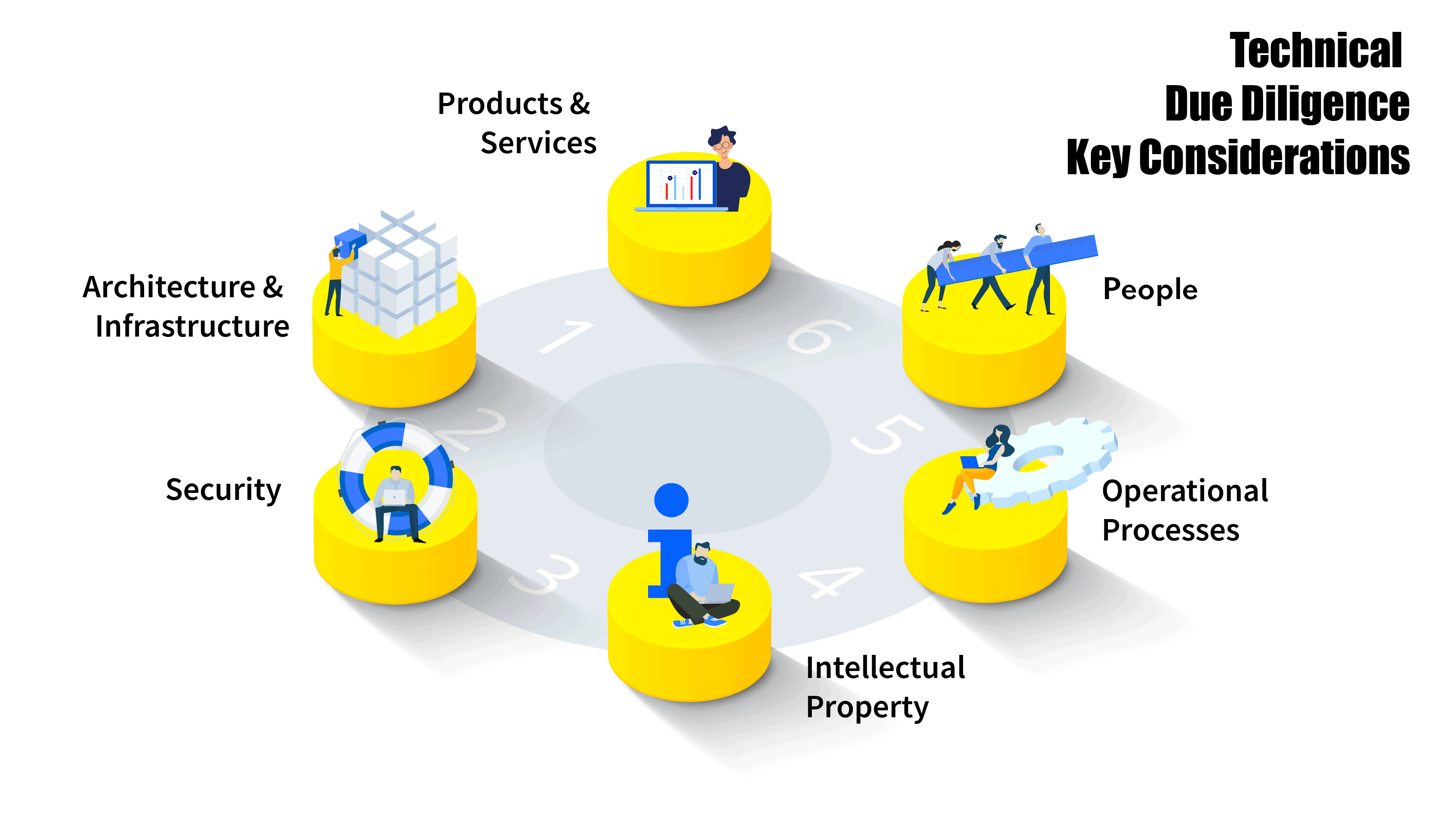
To ensure a thorough assessment of any organisation, I have adopted the following six-point framework to evaluate Business IT maturity. It takes into account the most crucial aspects of technical due diligence.
- Products and Services
- Architecture and Infrastructure
- Security
- Intellectual Property and Licences
- Operational Processes and Financial Health
- People
Let us delve into all six essential elements, assessing each individually to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Products and services
The first set of factors involves assessing your software products and services.
This process necessitates analysing technical specs and studies, conducting surveys, and demonstrations, validating code quality, on-site tests, and presenting market research and competitor analysis.
For maximum success, your team members must take the time to refine your tech roadmap and long-term organisation plans before beginning. Your documents should be comprehensive enough so readers can quickly grasp their scope, details, and budgetary projections for future enhancements or services.
The review’s scope may include examining how effectively data is being used to support intelligent decision-making.
For further reading on how data science transforms business outcomes, see my earlier post – Advanced Decision Intelligence: How to understand your data better than ever before.
Product technical due diligence checklist
-
-
- Does the product strategy align with your investment and growth objectives?
- Do you know if product design documents are up to date?
- How are the development team members resourced?
- How robust are the development and deployment processes? Could you tell me if product development follows these processes?
- Has a code review been performed?
- Are KPIs in place for the software development team?
- Are the system development processes effective and cost-efficient, and can they support your products’ continued development?
- Analysing the development code using various analytical tools allows you to glimpse the architectural design and code complexity.
-
Architecture & Infrastructure
The next consideration in my six-point framework is to review your enterprise architecture and infrastructure layout.
Be prepared to discuss the foundational tech solutions that make up your critical business systems. This includes architectural charts, scalability, performance indicators, programming languages, databases, application servers, and other associated tools. It is also essential to compare your tech and product with those offered by your competition; this will give you a clear picture of how they stack up.
Remember to mention open-source components, third-party tools, deployment and patching capabilities, configuration administration and build processes during your talk with the Tech Due Diligence team. If possible, demonstrate how they interoperate with existing standards and integrate effectively within other products in your ecosystem.
The Tech Due Diligence team’s objective is to evaluate your IT system in terms of effectiveness, sustainability, code quality, data quality, and the capacity for interconnection with other services.
Infrastructure Technical due diligence checklist
-
-
- Are there any challenges with the architecture that could prevent you from meeting growth objectives?
- Will existing infrastructure, processes, and practices scale appropriately with the company’s growth?
- What software system architecture is in use? (How robust is the code quality? It is monolithic, microservices, or serverless)
- Are there measurable indicators of the application system’s scalability and availability?
- Is the roadmap defined?
-
Security
Security is paramount when conducting technical due diligence, so it would be wise to prioritise this step before any tech assessment.
To secure your organisation, you should enlist the services of a company to test it for potential hacks, malware attacks, and fake accounts. This will ensure that your systems adhere to official software quality standards.
The Tech Due Diligence team will evaluate your security measures, adherence to rules and regulations, encryption, communication protocols, tokenisation, multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and data monitoring. They are also likely to cover quality assurance, security patching, system testing methods, deployment practices, code dependencies, and other accompanying procedures.
To ensure your company runs effectively and securely, employees must receive frequent training in security protocols, social engineering prevention methods, and compliance regulations.
Security technical due diligence checklist
-
-
- Are adequate security controls in place to protect customers and company data?
- Has the organisation achieved the security certifications required for its industry and client base?
- Is security testing routinely performed as part of developing source code?
- Do open-source development components present any security concerns?
- Do you know if there is a business continuity plan in place?
-
Intellectual Property & Licenses
Intangible assets significantly enhance your business value.
You should expect investors to rigorously evaluate your patents, copyrights, and trademarks to ensure that you have protected your products. Additionally, they want assurance that by acquiring the rights to these inventions, you won’t infringe on others’ legal ownership or run into potential conflicts with the law.
During the tech diligence process, you will need to be fully prepared by providing patent documentation that guarantees your intellectual property and validates that you did not transgress any other party’s intellectual property rights.
As part of your software documentation, you will be expected to provide an extensive report that contains all third-party components, including free and open-source details and commercial libraries – commonly referred to as an attribution report.
Intellectual property due diligence checklist
-
-
- Are all patent and patent applications (domestic and foreign) documented?
- Are third-party IT and open-source software licenses, including open-source components, in place? – It’s essential to safeguard your product’s elements, such as third-party integrations and open-source elements.
- What are the limitations on your patents, IT systems, and software licenses?
- What is your approach to intellectual property protection and enforcement?
-
Operational processes and financial health
The due diligence expert will carefully review your operating model and processes to determine your organisation’s maturity level. To ensure success, it is essential to be proactive in the documentation process; document all your organisation’s procedures and processes, individuals involved, resources required, and the costs incurred.
Financial due diligence is essential to any technical review. It involves reviewing costs and expenses incurred to service your business. This will include examining budgets against actual spending, capital expenditure (Cap-Ex) versus operating expenses (Op-Ex), software licence agreements, and human resource costs.
Financial due diligence also helps identify potential opportunities for profit or growth and can help eliminate inefficiencies and waste. By conducting rigorous financial due diligence, organisations can confidently make well-informed decisions.
Operational processes due diligence checklist
-
-
- Remembering that potential development code errors may expand project costs and extend deadlines is critical.
- What is the ratio of Cap-ex versus Op-ex spending?
- What are the direct costs associated with selling and delivering your product?
-
People
Ensuring your organisation chart is regularly maintained should be a priority. You may want to create a system cataloguing all staff members, including their roles, privileges, and any other pertinent information. Also, you should develop an outline of potential staffing or contractual investments needs; this will help you plan how best these positions can positively impact your organisation.
The interviewers may ask questions you didn’t anticipate, so you must ensure your personnel are adequately prepared for the meeting. Your CTO, CIO, project managers and architects should be equipped with detailed answers about your culture, internal policies, and sound reasoning behind their decisions.
People due diligence checklist
-
-
- Is there an up-to-date organisational chart in place?
- Does technical resourcing present any possible risks?
- What are the costs for full-time and contracted staff (for the last three years and current years)?
-

What are the challenges of tech due diligence?
Preparing for technical due diligence requires meticulous attention to detail.
Knowledgeable tech due diligence teams are accustomed to the process. They can detect any fault in your IT environment, inefficiencies, organisational roadblocks, or potential risks that could impact your company’s worth or jeopardise a real deal.
How long does a technical due diligence review typically take?
Technical due diligence typically lasts two to three weeks on average.
However, a review that has been poorly planned can take much more time to finish if no preparation has been done or the Tech Due Diligence team needs help getting access to the necessary information.
Conclusion
Technical due diligence is an essential part of any growth strategy. It enables businesses to identify potential risks before investing or any merger and acquisition and helps them make informed decisions about their tech investments.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, businesses can rest assured that they are taking all necessary precautions to ensure the success of their investments.
With a competent third-party expert performing the technical due diligence assessment, companies can be confident that they are making wise decisions and gaining maximum value from their investments.

PART III
Technical Due Diligence
A thorough and independent review of a business’s people, processes and technology.
Non Disclosure Agreement (NDA)
Protecting sensitive information is essential for successful business operations. That’s why NDAs, or confidentiality agreements, are vital legal contracts to ensure confidential details remain secure when shared with others.
Letters of Intent (LOI)
Letters of Intent are an essential stepping stone in the journey to a definitive agreement. They protect parties, outlining key terms and conditions before entering into binding legal contracts.
Monolithic Architecture
Monolith architectures are a traditional way of designing and building software. They are a single-tiered approach to software development, where components intertwine into one extensive application. Unsurprisingly, this can lead to extended codebases that require extra effort for long-term maintenance and upkeep.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices bring a revolutionary approach to software development, allowing for increased agility and scalability. By breaking down components into smaller, self-contained services with well-defined APIs, teams are empowered to independently develop & deploy their code without compromising the integrity of an entire system.
Serverless
Serverless is modernising how applications are developed and deployed – without developers worrying about managing servers. This cloud-native model allows for more seamless development as server tasks happen behind the scenes, leaving more time to focus on building great products.
Open-Source
Open source is a revolutionary concept, transforming the way the software operates. It makes code publicly available and accessible for anyone, allowing individuals to customise programs or create entirely new ones of their design with unprecedented freedom.
Frequently asked questions
How do you prepare for technical due diligence?
The key to preparation is maintaining a due diligence checklist that lists all the critical information and questions relevant to your firm.
For example:
- Keep documents up to date, including architecture and development documentation.
- Use a virtual data room for storing documentation.
- Implement a responsibility assignment chart (RACI).
- Prepare your managers and key employees for interviews so they can explain how your tech fits into your overall organisation.
- Audit your systems annually.
- Hire a team to assess your IT.
What are the three principles of due diligence?
- Verify & Identify
- Understanding the organisation
- Being Vigilant
What are the three types of diligence?
- Financial
- Commercial
- Legal
What is technical due diligence construction?
Technical due diligence construction helps identify potential risks by thoroughly examining a physical site and determining its appropriateness.
What is technical due diligence in M&A?
Technical due diligence in M&A is where an acquiring company assesses its target’s IT architecture and seeks to identify any possible risks/issues as to why the deal should not go ahead.
What is an example of due diligence?
An insurance company interested in taking over a new Insurer is an excellent example of due diligence. Its mergers and acquisitions department will perform due diligence, including conducting a comprehensive investigation of the entity while remaining as objective as possible with its findings.
References
The Essentials: Characteristics of Due Diligence (Unknown). In OCED.
Support for due diligence (Unknown). In ICAEW.
Due diligence (2020, October 7). In CIOB ORG.
What is due diligence? (2022, May 30). In Contractbook.
4 Key Elements of Technical Due Diligence (2021, October 14). In FOSSA.
What is technical due diligence? (Unknown). In snyk.
Technical Due Diligence for Start-ups: Preparation Checklist (2022, December). In Altigee Magazine.
Technical Due Diligence: Meaning, Process and Checklist (2022, December 9). In djangostars.
Technical Due Diligence (Unknown). In TFT.
Top Tips for Technical Due Diligence Process (2021, May 27). In MEND.
Technology Due Diligence Checklist (Unknown). In Halo Lab.
All You Need to Know About Technical Due Diligence for Start-Ups (2022, September 9). In Cleveroad.
Is Your Tech Due Diligence Good Enough? (2022, March 7). In Bain.
Increase efficiency to maximise your profit (Unknown). In NI Business Info.
4 Actions to Ensure Your Tech Investments Pay Digital Dividends in 2023 (Unknown). In Gartner.






